Global Innovation Index : The Malaysia Chapter
Announcment!
Global Innovation Index 2023
" Innovation in the face of uncertainty "

GII Inforgraphic
Save the Date: September 27, 2023 – Release of the Global Innovation Index 2023
The 16th edition of WIPO’s Global Innovation Index (GII) will be released on Wednesday, September 27, 2023 during a hybrid event from 13:30 to 15:30 p.m. CEST (Geneva time) or 19:30 to 21:30 p.m. GMT (Malaysia time) featuring ministers, business leaders, and innovation experts. Key findings of the GII 2023 will be presented, followed by a panel discussion on “Innovation in the face of uncertainty”.
- 0Days
- 0Hours
- 0Minutes
- 0Second
"KUALA LUMPUR, 11th September 2023 - Prime Minister Datuk Seri Anuar Ibrahim also know as PMX today presented the Mid-Term Review (MTR) of the 12th Malaysia Plan (12MP) at the Dewan Rakyat. The theme of the review is 'Malaysia Madani: Sustainable, Prosperous, High-Income,'. PMX has set a new Global Innovation Index (GII) target for Malaysia to rank 30th out of 132 economies by 2025.
Intro to Webpage GII
Webpage Global Innovation Index (GII): The Malaysia Chapter is now live!
Hello! GII's.
Welcome to the Webpage Global Innovation Index : The Malaysia Chapter , your one-stop destination for insights into the world of innovation! We are excited to present a comprehensive platform that sheds light on the transformative power of innovation across the globe.
Source : https://mastic.mosti.gov.my
The Global Innovation Index, or GII is a pioneering initiative brought to you by a collaborative effort between the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Cornell University, and INSEAD. This index serves as a crucial benchmark, evaluating and ranking the innovative capabilities of nations worldwide, especially Malaysia.
At our Webpage, we have assembled a wealth of information, data, and analyses about Malaysia's and the world's current status to help you understand the multifaceted dimensions of innovation. Explore the latest rankings of countries, delve into annual reports, and gain valuable insights into global innovation trends and best practices.
Our Webpage delves into a multitude of factors that contribute to innovation, ranging from research and development to investments in education, infrastructure, and technology. We also assess entrepreneurial activities and the protection of intellectual property, among many other essential aspects.
By providing this comprehensive overview, we aim to offer a clear perspective on how innovation can drive our nation (Malaysia) to positive change in various economic and social sectors. Nations that excel in the GII rankings are known for fostering innovation-friendly environments, leading to the development of cutting-edge technologies and solutions that impact society and economies in profound ways.
Policymakers, business leaders, researchers, and curious minds can all benefit from our Webpage's extensive data. Through GII, we hope Malaysians to foster a better understanding of the pivotal role innovation plays in shaping the trajectory of countries and offer valuable insights to enhance the quality of life and global competitiveness.
News & Events Calendar
KEEP UPDATE ON GII MALAYSIA
UPCOMING NEWS & EVENTS
Source:
https://mastic.mosti.gov.my
What Is The Global Innovation Index?
Source : www.wipo.int
Workshop on Coordination of Initiative Input for the Global Innovation Index among 26 Ministries/Entities of Malaysia
Source : https://mastic.mosti.gov.my

The 12MP or RMKe-12
The 12MP or RMKe-12
The Twelfth Malaysia Plan otherwise known as the 12th Malaysia Plan and abbreviated as "12MP" or (Malay: Rancangan Malaysia Kedua Belas - RMke-12), is a comprehensive blueprint prepared by the Economic Planning Unit (EPU) of the Prime Minister's Department (PMO) and the Ministry of Finance. You can find more information about the GII in 12MP here specifically in [p.342, p.348, p.387, p.388 & p.391].
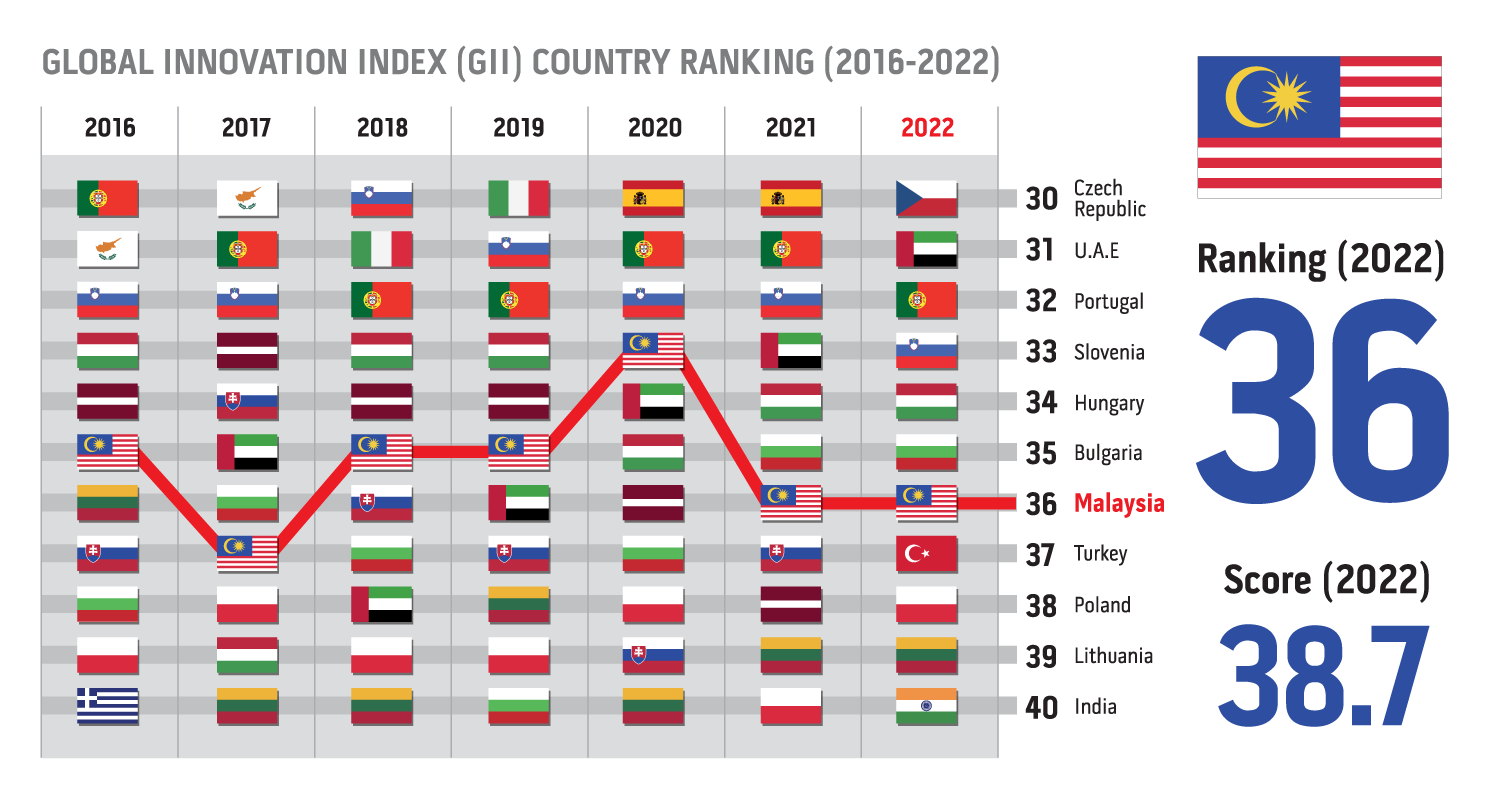

GII Monitoring System also known as "Model Data Global Innovation Index"
GII Monitoring System also known as "Model Data Global Innovation Index"
The Global Innovation Index (GII) monitoring system called as "Model Data Global Innovation Index" is a tool that was specifically developed to track Malaysia’s GII scores & ranking from the past year since 1996 to the next foresight year ahead. The system is managed by MASTIC-MOSTI and MIGHT (Strategic Partner) in the Jawatankuasa Inter-Agensi Pemantauan Daya Saing GII (JIPGII), which is a committee established by the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MOSTI). The purpose of the system is to monitor Malaysia’s past performance, country benchmarking, details of indicator information, simulation of data/scenarios that have the potential to predict and subsequently improve the country’s position, and tracking to track the year used for each indicator for Malaysia and to compare/monitor targets and actual data from time to time. You can find more information about the Portal called System Model Data GII HERE.
We invite you to embark on an exciting journey of discovery with the Webpage Global Innovation Index: Malaysia Chapter. Whether you're seeking to learn, analyze, or collaborate, we are here to empower your understanding of the world of innovation.
Top 10: The World’s Most Innovative Countries – Global Innovation Index 2023.
In the Global Innovation Index for 2023, Switzerland remains at the forefront, securing the 1st position for the 13th consecutive year. Sweden holds steady in 2nd place, while the United States slips to 3rd from its 2nd-place ranking in 2022. The United Kingdom maintains its 4th position, while Singapore climbs from 7th to 5th place. Finland drops to 6th, and the Netherlands moves to 7th from 5th. Germany retains 8th place, Denmark rises from 10th to 9th, and the Republic of Korea falls to 10th from 6th in the previous year. In summary, Switzerland, Sweden, and the United States remain innovation leaders, but there have been notable shifts in rankings, with Singapore and the Republic of Korea experiencing significant changes.
Source : www.wipo.int
GII Reports Summary
2022
2022 GII Report
The 2022 Global Innovation Index
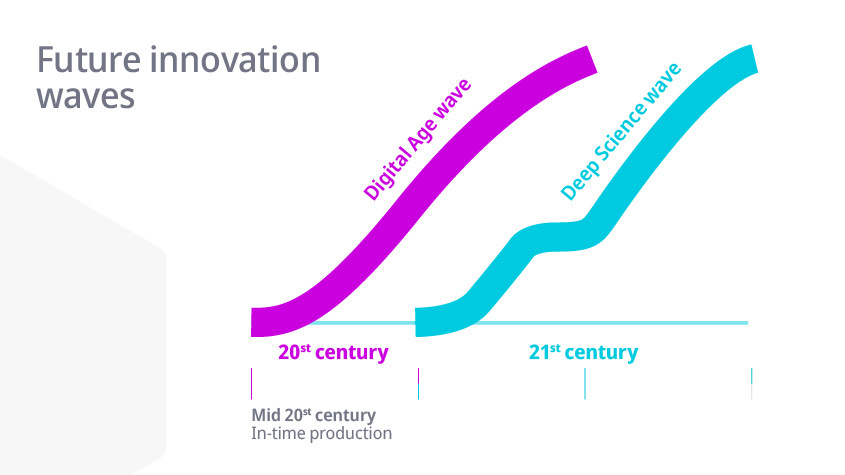
The main objective of the Global Innovation Index (GII) reports 2022 is to track the most recent global innovation trends against the background of an ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, slowing productivity growth and other evolving challenges. The GII reports 2022 aim to provide a comprehensive and multi-dimensional measure of innovation performance for 132 economies, highlighting their innovation strengths and weaknesses. The GII reports 2022 also focus on the future of innovation-driven growth, exploring whether stagnation and low productivity growth are here to stay, or whether we are about to enter a new era,
 Source : www.wipo.int
Source : www.wipo.int
where new innovation spurts - the Digital Age and the Deep Science Innovation waves - bring about an economic uplift. The GII reports 2022 offer insights and recommendations for policymakers, business leaders, innovators and researchers on how to foster innovation and leverage its potential for sustainable and inclusive development.
Top 10: The World’s Most Innovative Countries – Global Innovation Index 2022
Switzerland, U.S., Sweden, United Kingdom and the Netherlands are the world’s most-innovative economies according to WIPO's Global Innovation Index 2022.
Source : www.wipo.int
Website GII
About GII Science and Technology Clusters 2022
The GII Science and Technology Clusters are identified based on patent filings and scientific article publications, revealing areas worldwide with the highest concentration of inventors and authors. WIPO employs geocoding to accurately map these clusters. These clusters are part of the broader Global Innovation Index (GII), which assesses global innovation trends annually. The GII evaluates the innovation performance of countries, highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in innovation metrics. It incorporates approximately 80 indicators, including factors like the political environment, education, infrastructure, and knowledge creation in each economy. The GII serves as a tool for monitoring and comparing performance against economies in the same region or income group.
East Asia Takes Leading Position in Global Science & Technology Clusters on the Global Innovation Index
In the Global Innovation Index's latest release, it was found that four of the world's five largest science and technology clusters are located in East Asia, specifically in Japan, China (two clusters), the Republic of Korea, and the United States. This information comes from an early preview of the 2022 edition of the Global Innovation Index (GII) by WIPO. The GII assesses the innovation capabilities of about 130 countries and economies worldwide annually. In a pre-release ahead of its official launch on September 29, 2022, the GII 2022 S&T Clusters Chapter focuses on identifying regions with the highest concentration of science and technology development. The Tokyo-Yokohama cluster is the largest, followed by the Shenzhen-Hong Kong-Guangzhou, Beijing, Seoul, and San Jose-San Francisco clusters. When considering population proportion, the Cambridge cluster in the United Kingdom and the Eindhoven area in the Netherlands/Belgium are the most science and technology-intensive clusters, followed by Daejon in the Republic of Korea, San Jose-San Francisco, and Oxford, UK. Local innovation clusters play a crucial role in national innovation ecosystems, fostering innovation, jobs, investments, and growth. In addition to well-established clusters in the U.S., Europe, Japan, and the Republic of Korea, new science and technology hubs are emerging in East Asia, particularly in China, as well as in other middle-income economies like Brazil, India, Iran, Türkiye, and elsewhere. WIPO Director General Daren Tang commented on these findings.
In additional findings, the United States features prominent science and technology clusters in San Jose-San Francisco, Boston-Cambridge, and New York City. In Europe, the leading clusters are located in Paris, London, and Cologne. Notably, China now boasts as many top science and technology clusters as the United States, each with 21 clusters. Germany hosts 10 such clusters, while Japan has five. The 2022 cluster rankings saw significant increases in several regions compared to the previous year. China experienced substantial growth with clusters in Zhengzhou (+15 positions), Qingdao (+12), and Xiamen (+12) showing remarkable progress. Other notable increases were seen in Berlin (+4) in Germany, Istanbul (+4) in Türkiye, Kanazawa (+4) in Japan, Ankara (+3) in Türkiye, Daegu (+3) in the Republic of Korea, and Mumbai (+3) in India.
Source : www.wipo.int
Global Innovation Index 2022: What You Need to Know by WIPO
Source : www.wipo.int
An overview of the key findings of the Global Innovation Index (GII) 2022
Switzerland, the United States, Sweden, the United Kingdom and the Netherlands are the world’s most-innovative economies, the GII finds, with China on the threshold of the top 10. Other emerging economies are also showing consistently strong performance, including India and Türkiye, both of which enter the top 40 for the first time. Published on 29 September 2022, the GII 2022 ranks the innovation performance of 132 countries and economies around the world. Themed "What is the future of innovation-driven growth?", this year’s edition focuses on the effect of innovation on productivity and wellbeing of society over the coming decades.
#WIPO #GlobalInnovationIndex #GII2022 #Innovation
2023
Current Year 2023 GII Report
The 2023 Global Innovation Index
Who leads on unicorns?
The 2023 Global Innovation Index (GII) introduces a new indicator: 6.2.2 Unicorn valuation, % GDP that assesses the combined valuation of unicorn companies, which are privately held startups valued at over USD 1 billion. These unicorns are known for their rapid growth and disruptive innovations that can reshape entire industries. As of April 2023, there were 1,206 unicorn companies across 50 countries worldwide.
Key findings from the GII report regarding unicorn companies include:
1. Global Distribution: Unicorn companies are primarily concentrated in five economies, with the United States hosting 54% of them, followed by China (14%), India (6%), the United Kingdom (4%), and Germany (2%). The total valuation of unicorn companies globally in 2023 reached USD 3.8 trillion, with US unicorns accounting for USD 2 trillion, followed by China at USD 736 billion and India at USD 193 billion.
2. Top Valuable Unicorns: Among the top 25 most valuable unicorn companies, China leads with ByteDance (1st in artificial intelligence), SHEIN (3rd in e-commerce), and Xiaohongshu (12th in e-commerce). The United States follows with SpaceX (2nd in space and telecommunications), Stripe (4th in fintech), and Epic Games (7th in video games). Other countries like Australia and Indonesia also have notable unicorn companies.
3. Scaling by GDP: The GII scales the cumulative value of unicorns by GDP to assess the unicorn ecosystem's relative strength in different economies. Five economies, namely Estonia, Israel, Lithuania, Senegal, and the United States, tie for the top position after scaling. These countries are home to unicorns like Bolt, Wiz, Vinted, and Wave, operating in various sectors.
4. Unicorns and Development: Analyzing the relationship between an economy's level of development and the cumulative value of its unicorn companies reveals that most high-income economies fall in the upper-right quadrant. However, there are also high-income European economies with a lower concentration of unicorn companies in the lower-right quadrant.
In summary, the GII report highlights the prevalence and economic significance of unicorn companies globally, with a focus on their concentration in a few leading economies and their impact on innovation and economic development.
Unicorn valuation by level of economic development, 2023
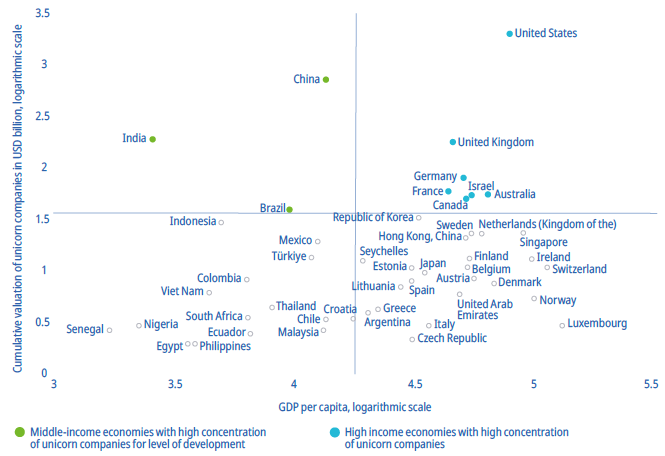
Source : Authors, based on CBInsights, 2023 and IMF World Economic Outlook, April 2023.
The left-hand quadrants in the analysis of unicorn companies in relation to economic development reveal some intriguing cases:
1. Upper-Left Quadrant: This quadrant includes middle-income economies like China, India, and Brazil. These countries stand out as they have a high concentration of unicorn companies relative to their level of development. It indicates that they are fostering a vibrant ecosystem of innovative startups, despite not being high-income nations.
2. Lower-Left Quadrant: In this quadrant, you find middle- and low-income economies that host unicorn companies, even though their valuations might be comparatively lower. Notably, Latin American economies feature prominently in this category, including Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, and Mexico. Some of the leading unicorns from this region include Kavak (Mexico, e-commerce), Rappi (Colombia, supply chain), and Uala (Argentina, fintech).
These findings underscore the dynamic and diverse landscape of unicorn companies worldwide, with some emerging economies punching above their weight in nurturing innovative startups, particularly in Latin America.
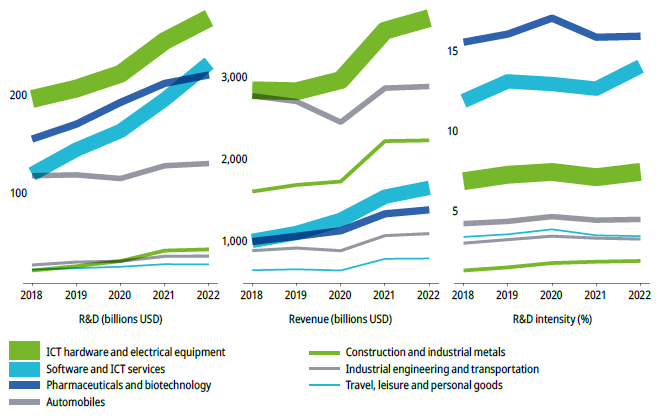
Source : WIPO, based on BvD Orbis database.
In 2022, the United Kingdom witnessed a decline in the number of companies increasing their R&D budgets compared to the exceptional year of 2021, with one notable exception being the travel, leisure, and personal goods sector, where more firms increased their R&D spending. Pharma led the R&D intensity ranking in 2022 at 15.9 percent, followed closely by software and ICT services at 14.1 percent, significantly ahead of ICT hardware at 7.4 percent and automobiles at 4.5 percent. Among the top 15 firms in the top seven industries, most increased their R&D expenditures in 2022, except for pharmaceuticals, industrial engineering, and transportation. The ICT hardware sector saw impressive R&D growth, led by Nvidia, SK Hynix, and Mediatek. In software and ICT services, Meta and Uber showed substantial R&D growth, while the automobile sector also displayed positive trends, with General Motors, Volkswagen, and Robert Bosch leading in expenditure. Additionally, the travel, leisure, and personal goods sector saw notable R&D spending growth, with companies like Roblox, Unity Software, and Airbnb making strides.
About GII Science and Technology Clusters
The Global Innovation Index's Science and Technology (S&T) Cluster ranking identifies regions with concentrated science and technology activity. These clusters are determined by analyzing patent filings and scientific publications to locate areas with a high density of inventors and authors.
WIPO locates and ranks science and technology clusters through a geocoding method, mapping addresses and names pulled from documents to 96% accuracy. Find out more about the S&T Cluster methodology.
The top five S&T clusters in the world are all in East Asia, with Tokyo-Yokohama (Japan) leading, followed by Shenzhen-Hong Kong-Guangzhou (China and Hong Kong), Seoul (Republic of Korea), Beijing (China), and Shanghai-Suzhou (China).
The United Kingdom's Cambridge cluster and San Jose-San Francisco in the United States exhibit the most intensive S&T activity relative to population density, followed by Oxford (UK), Eindhoven (Netherlands), and Boston-Cambridge (US).
China has the most S&T clusters, with 24 identified this year, followed by the US with 21, Germany with 9, and Japan, Canada, India, and the Republic of Korea each having 4. Notable clusters include San Jose-San Francisco (US), Munich (Germany), Tokyo-Yokohama (Japan), Toronto (Canada), Bengaluru (India), and Seoul (Republic of Korea).
Middle-income economies like India also experienced significant growth in S&T clusters, particularly in Chennai and Bengaluru. Emerging economies such as Brazil, India, Türkiye, Argentina, Egypt, and Thailand witnessed rapid growth in their S&T clusters.
Source : www.wipo.int
Global Innovation Index 2023: What You Need to Know by WIPO
Source : www.wipo.int
An overview of the key findings of the Global Innovation Index (GII) 2023
The Global Innovation Index (GII) report for this year provides valuable insights into the evolving global innovation landscape, which is influenced by factors like the ongoing pandemic, geopolitical shifts, and economic recovery. It's important to note that some of the changes in GII rankings this year may be influenced by short-term trends rather than long-term shifts. Key takeaways from the report include:
1. Shifts Among Top 20 Innovators: Notable changes have occurred among the top 20 innovating countries. Sweden, Singapore, Finland, Denmark, France, and Israel have moved up the rankings, with a strong performance by Nordic and Baltic nations.
2. Mixed Picture for Emerging Economies: Leading emerging economies display a mixed performance. Indonesia has seen rapid growth, the Philippines and Vietnam are progressing, while India remains stable. However, China, Turkey, and Iran have experienced slight declines, possibly due to COVID-19 effects.
3. Consistent Overperformance: India, the Republic of Moldova, and Vietnam have consistently outperformed in innovation relative to their development levels for 13 years. Indonesia, Uzbekistan, and Pakistan have maintained their overperformer status, with Brazil overperforming for three consecutive years.
4. Positive Developments in the Middle East: The Middle East shows positive innovation ranking developments, with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) nearing the top 30. Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, Oman, and neighboring countries are making progress.
5. African Innovation Leaders: Mauritius and South Africa lead innovation in Sub-Saharan Africa, with strong positions in the GII's top 60. Five economies in the region are overperforming in innovation, with Rwanda consistently doing so.
6. Need for Systematic Improvement: Many middle- and low-income economies could benefit from systematic and gradual improvements to their innovation ecosystems. Addressing challenges like pandemic impacts, limited risk capital, high interest rates, debt levels, and supply chain disruptions is crucial.
7. Monitoring and Preservation: Continuous monitoring of innovation trends is essential, especially in the context of sustainable development goals (SDGs). It is crucial to preserve the positive changes achieved in innovation systems and policies over the past two decades.
8. Future GII Reports: Future editions of the GII will closely track developments and their long-term impacts. This ongoing effort aims to enhance our understanding of innovation and its measurement, distinguishing between transient and enduring changes in country and regional performance.
In summary, the GII report highlights the dynamic nature of global innovation, influenced by a range of factors. While some changes may be temporary, ongoing monitoring and policy adjustments are critical to maintaining and enhancing innovation ecosystems worldwide.
#WIPO #GlobalInnovationIndex #GII2023 #Innovation

GII Conceptual Framework
Conceptual Framework for the Global Innovation Index 2022
The overall GII ranking is based on two sub-indices that are both equally important in presenting a complete picture of innovation; the Innovation Input Sub-Index and the Innovation Output Sub-Index.
Each of the five (5) input and two (2) output pillars is divided into three sub-pillars, each of which is composed of individual indicators – a total of 81 this year (see the Economy profiles section for the Framework of the Global Innovation Index 2022).
A detailed elaboration of the conceptual framework and pillars can be found in the 2020 edition of the GII. Each sub-pillar is calculated by taking the weighted average of its individual indicators’ scores, which are normalized to again produce scores between 0 and 100.
Pillar scores are calculated using the weighted average of each pillar’s sub-pillar scores.
Hence, three indices are calculated:
01
Innovation Input
Sub-Index
Five input pillars capture elements of the economy that enable and facilitate innovative activities.
02
Innovation Output
Sub-Index
Two Innovation outputs pillars are the result of innovative activities within the economy.
03
The overall
GII score
Is the average of the Input and Output Sub-Indices, on which the GII economy rankings are produced.
Definitions of the pillars and what they evaluate:
5
Input Pillar
Innovation Input
Sub-Index
The first sub-index of the GII, the Innovation Input Sub-Index, has five enabler pillars: Institutions, Human capital and research, Infrastructure, Market sophistication, and Business sophistication. Enabler pillars define aspects of the environment conducive to innovation within an economy.
- Pillar 1:Institutions
- Pillar 2:Human capital and research
- Pillar 3:Infrastructure
- Pillar 4:Market sophistication
- Pillar 5:Business sophistication
Institutions
It evaluates the quality and effectiveness of various institutions within a country's innovation ecosystem that play a crucial role in fostering and supporting innovation. It is designed to measure the enabling environment for innovation within a nation. Assessing the state of institutions within a country allows the GII to gauge the overall environment for innovation and identify areas where improvements or policy changes can enhance the innovation ecosystem and promote economic growth and development.
Sub-Pillars:
- Political environment
- Regulatory environment
- Business environment
Human capital and research
This pillar evaluates the availability and quality of human capital, as well as the research and development (R&D) activities within a nation. By evaluating the state of human capital and research within a country, the GII can provide insights into the country's capacity to innovate, the effectiveness of its educational systems, and the extent of its research and development activities. This information is essential for policymakers, businesses, and institutions in identifying strengths and weaknesses in the innovation ecosystem and formulating strategies to foster innovation and drive economic growth and competitiveness
Sub-Pillars:
- Education
- Tertiary education
- Research and development (R&D)
Infrastructure
This pillar evaluates the quality and effectiveness of infrastructure, both physical and digital, within a nation, as these factors play a critical role in supporting innovation and economic development. By assessing the state of infrastructure within a country, the GII provides valuable insights into its capacity to support innovation and create an enabling environment for businesses, entrepreneurs, and researchers to thrive. Strong and reliable infrastructure can enhance connectivity, facilitate knowledge sharing, attract investments, and ultimately contribute to a more innovative and competitive economy.
Sub-Pillars:
- Information and communication technologies (ICTs)
- General infrastructure
- Ecological sustainability
Market sophistication
This pillar evaluates the level of market sophistication and the effectiveness of market mechanisms in supporting innovation-driven activities and economic growth. By evaluating the level of market sophistication within a country, the GII provides insights into the country's readiness to adopt and absorb innovative technologies and solutions. A sophisticated market environment with skilled workers, supportive business conditions, and ample funding opportunities can stimulate innovation, attract investments, and foster a thriving ecosystem of innovation-driven enterprises.
Sub-Pillars:
- Credit
- Investment
- Trade, diversification, and market scale
Business sophistication
This pillar evaluates the sophistication of business activities and practices within a nation, with a focus on aspects that support innovation and entrepreneurship. By assessing the level of business sophistication within a country, the GII provides insights into the innovation readiness and capabilities of businesses. A sophisticated business environment that encourages R&D investments, fosters creativity, and supports entrepreneurship can stimulate innovation-driven growth, foster competitiveness, and contribute to the overall development of a knowledge-based economy.
Sub-Pillars:
- Knowledge workers
- Innovation linkages
- Knowledge absorption
2
Output Pillar
Innovation Output
Sub-Index
Innovation outputs are the results of innovative activities within the economy. Although the Output Sub-Index includes only two pillars, it has the same weight in calculating the overall GII scores as the Input Sub-Index. There are two output pillars: Knowledge and technology outputs and Creative outputs. Although the Output Sub-Index includes only two pillars, it has the same weight in calculating the overall GII scores as the Input Sub-Index.
Knowledge and technology outputs
This pillar evaluates the tangible outcomes of a country's innovation efforts and the knowledge-intensive activities that contribute to technological advancement and economic growth. By assessing the knowledge and technology outputs of a country, the GII provides insights into the impact and effectiveness of its innovation ecosystem. A strong performance in this pillar demonstrates a country's ability to generate new knowledge, technological solutions, and intellectual property, which are essential drivers of economic competitiveness and sustainable growth. Additionally, a country's capacity to contribute to the global knowledge pool and attract international recognition further enhances its status as an innovative and dynamic player in the global economy.
Sub-Pillars:
- Knowledge creation
- Knowledge impact
- Knowledge diffusion
Creative outputs
This pillar evaluates the creative aspects of a country's innovation ecosystem, focusing on the generation and utilization of creative products and outputs. By assessing the creative outputs of a country, the GII provides insights into its ability to foster and capitalize on creativity as a driver of innovation and economic development. A strong performance in this pillar indicates a vibrant creative sector, the capacity to produce and market cultural and creative products, and the potential to leverage creative assets for economic growth and cultural enrichment. Emphasizing creative outputs can contribute to the overall innovation ecosystem and enhance a country's competitiveness in the global creative economy.
Sub-Pillars:
- Intangible assets
- Creative goods and services
- Online creativity
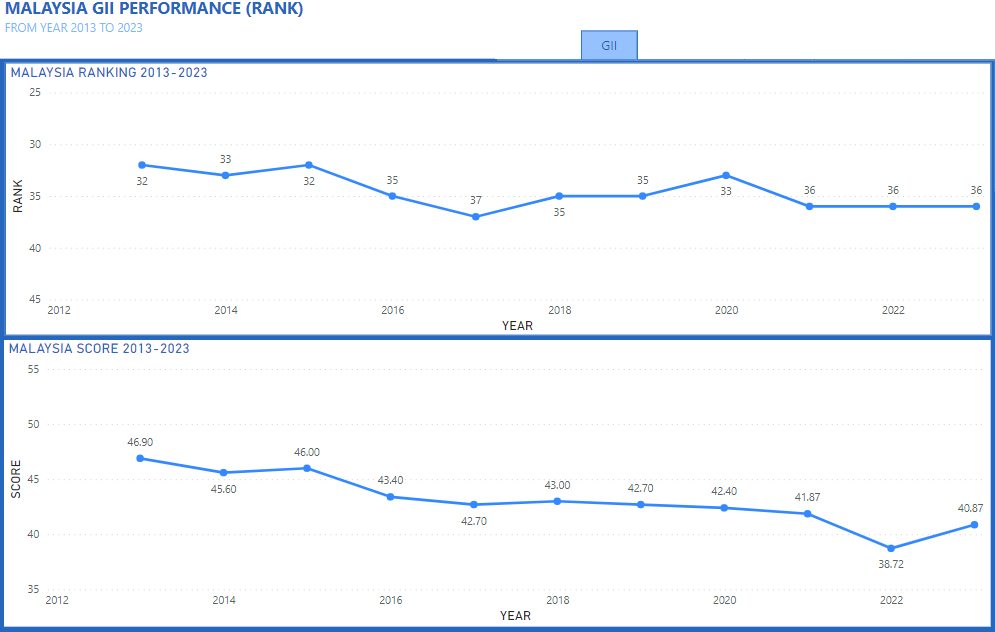
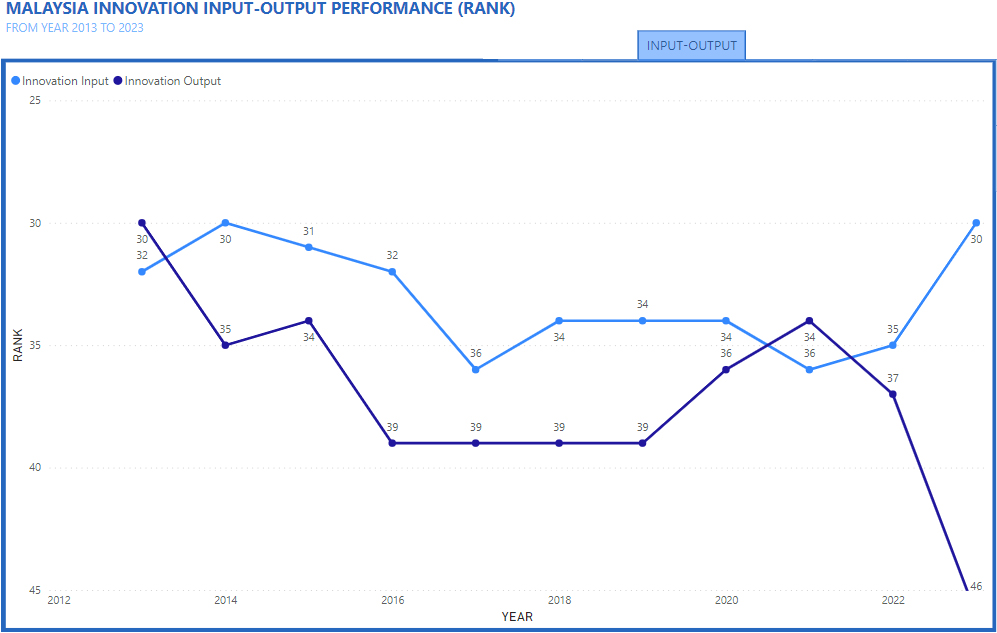
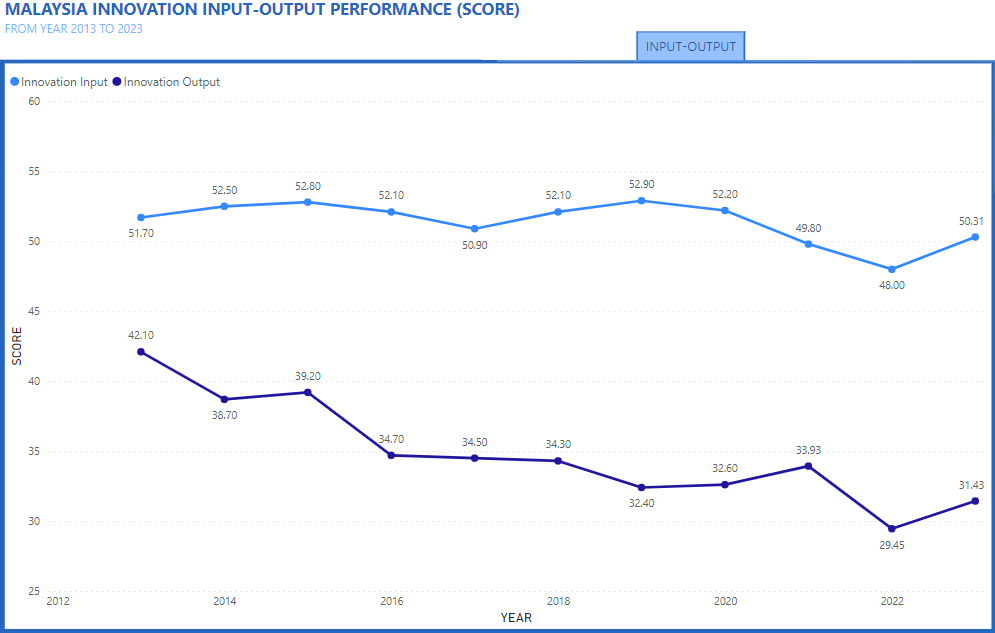
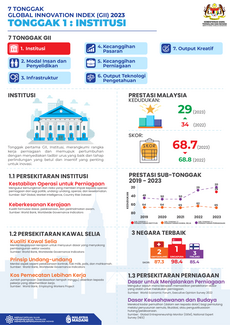
Malaysian GII Overview
An Overview of the Global Innovation Index for Malaysia(2013-2022)
#data entry GII 2023 is in progress
Here is a simplified interactive GUI dashboard that shows an overview of the Malaysia Global Innovation Index measured and ranked in 10 years based on GII reports between the years 2013 and 2022. It typically covers various aspects related to innovation performance, including institutions, human capital and research, infrastructure, market sophistication, business sophistication, knowledge and technology outputs, and creative outputs published by the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and its partners, which are typically released in September each year. This report provides a detailed analysis of Malaysia's innovation performance, its strengths and weaknesses, and its ranking. It also highlights specific indicators and factors contributing to Malaysia's innovation ecosystem. To get the most accurate and up-to-date information, we recommend checking the official WIPO website for the Global Innovation Index Report, All Edition.
Source : MIGHT Malaysia
Source : MASTIC Portal
Instagram:Ada Apa Dengan GII?
Malaysian GII Analysis
#Latest data GII 2023 available
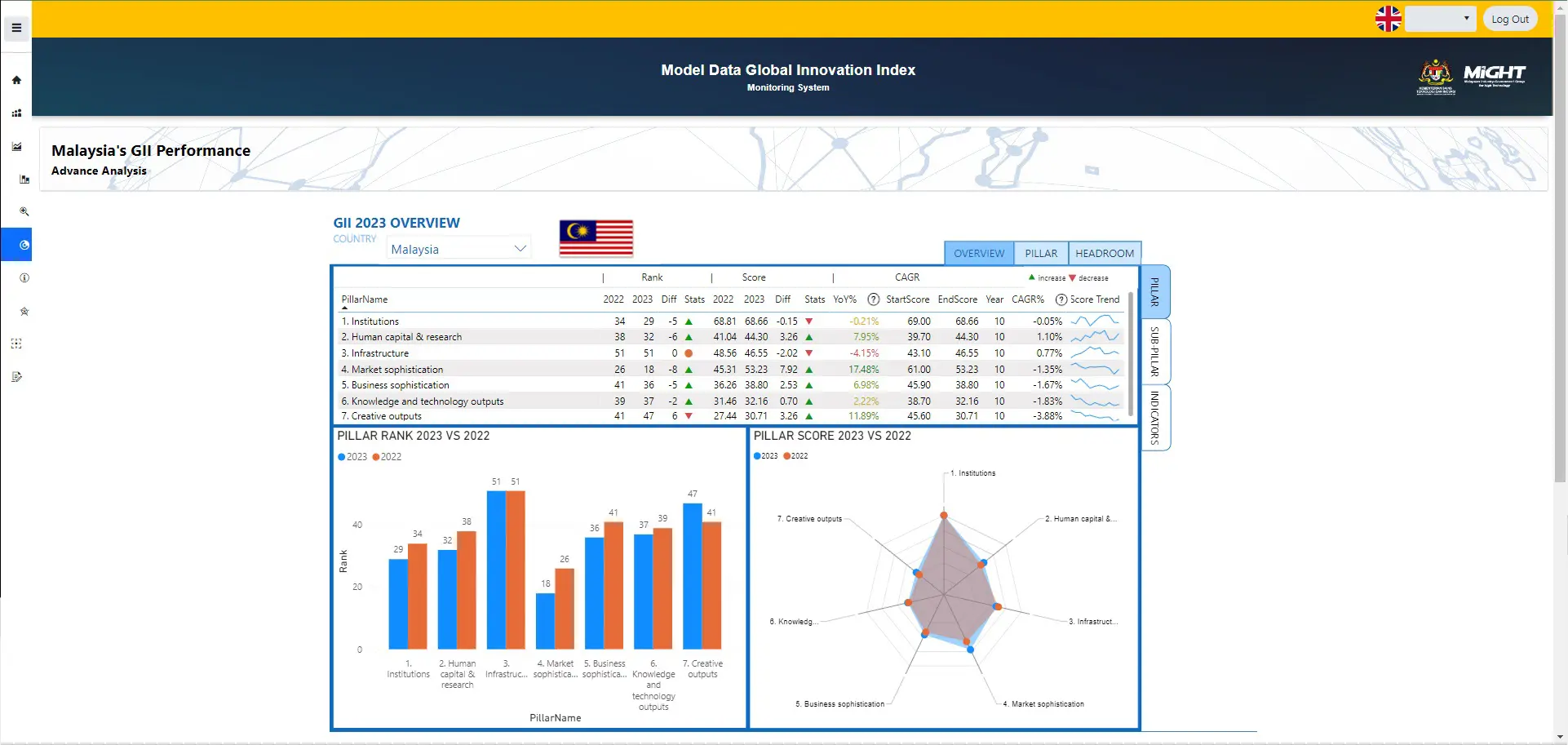
GII Data Analysis
Advance Analysis is used to access detailed reports on the analysis of pillars, sub-pillars, and indicators, performance of indicators compared to the previous year, and headroom availability for… Read More
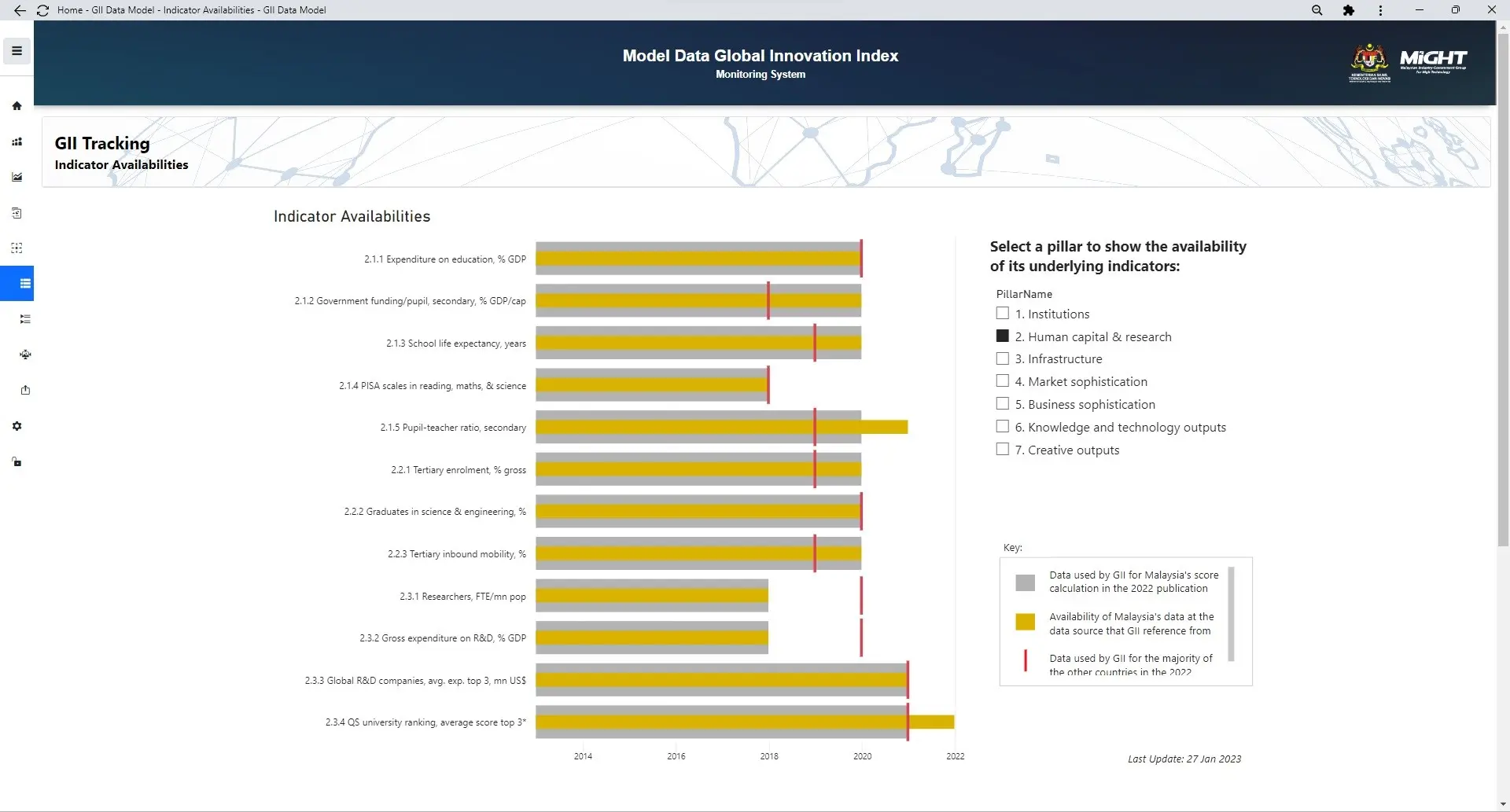
GII Indicator Data Availabilities
Module Tracking is a module for storing information regarding the availability years for each GII indicator of Malaysia and the years utilized by other countries. This module is intended to track… Read More
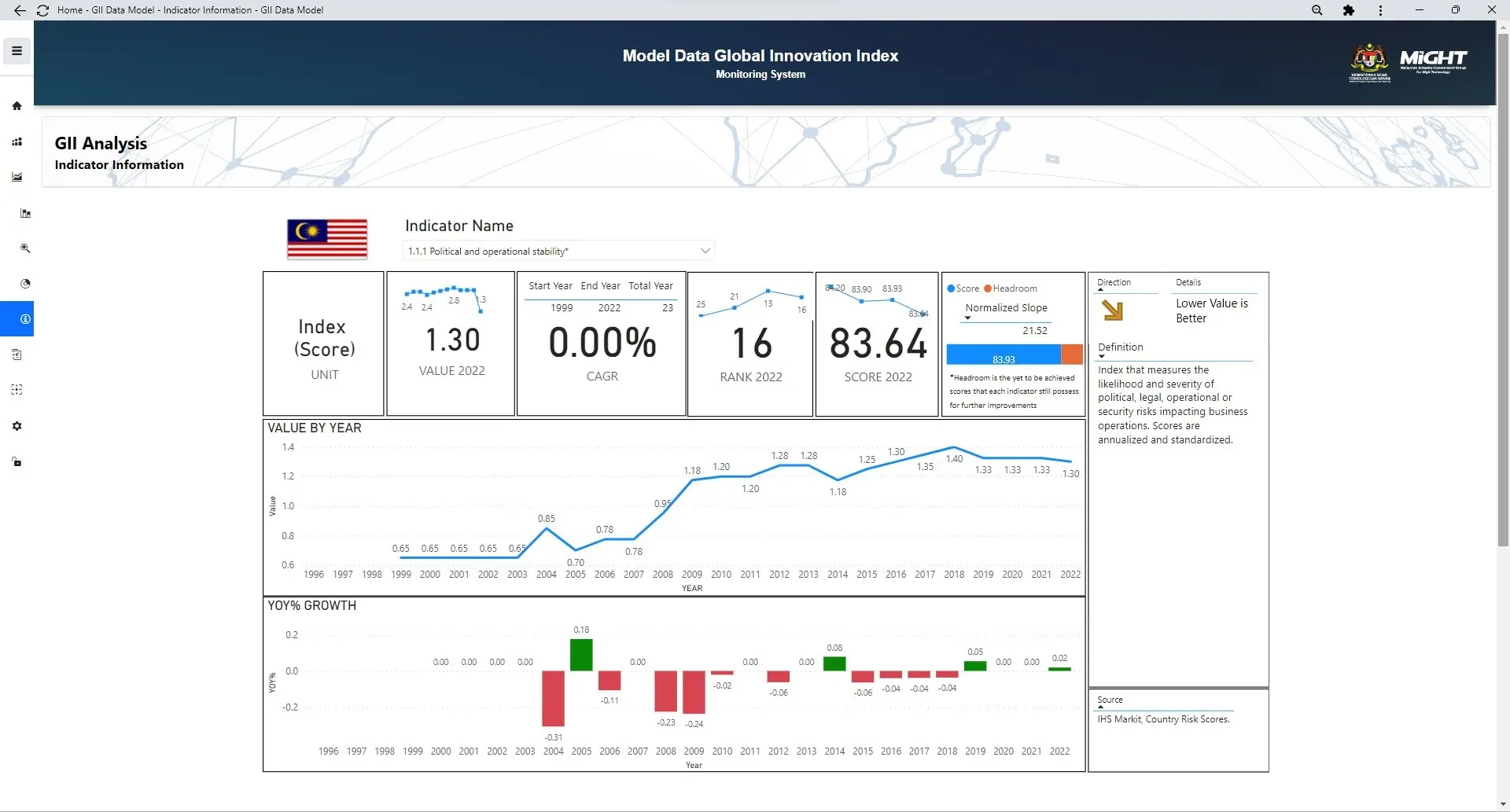
GII Indicator information
This module enables registered users to access detailed reports for each indicator, such as data trends, rankings, and scores for the latest year, normalized slope, available headroom, and also… Read More
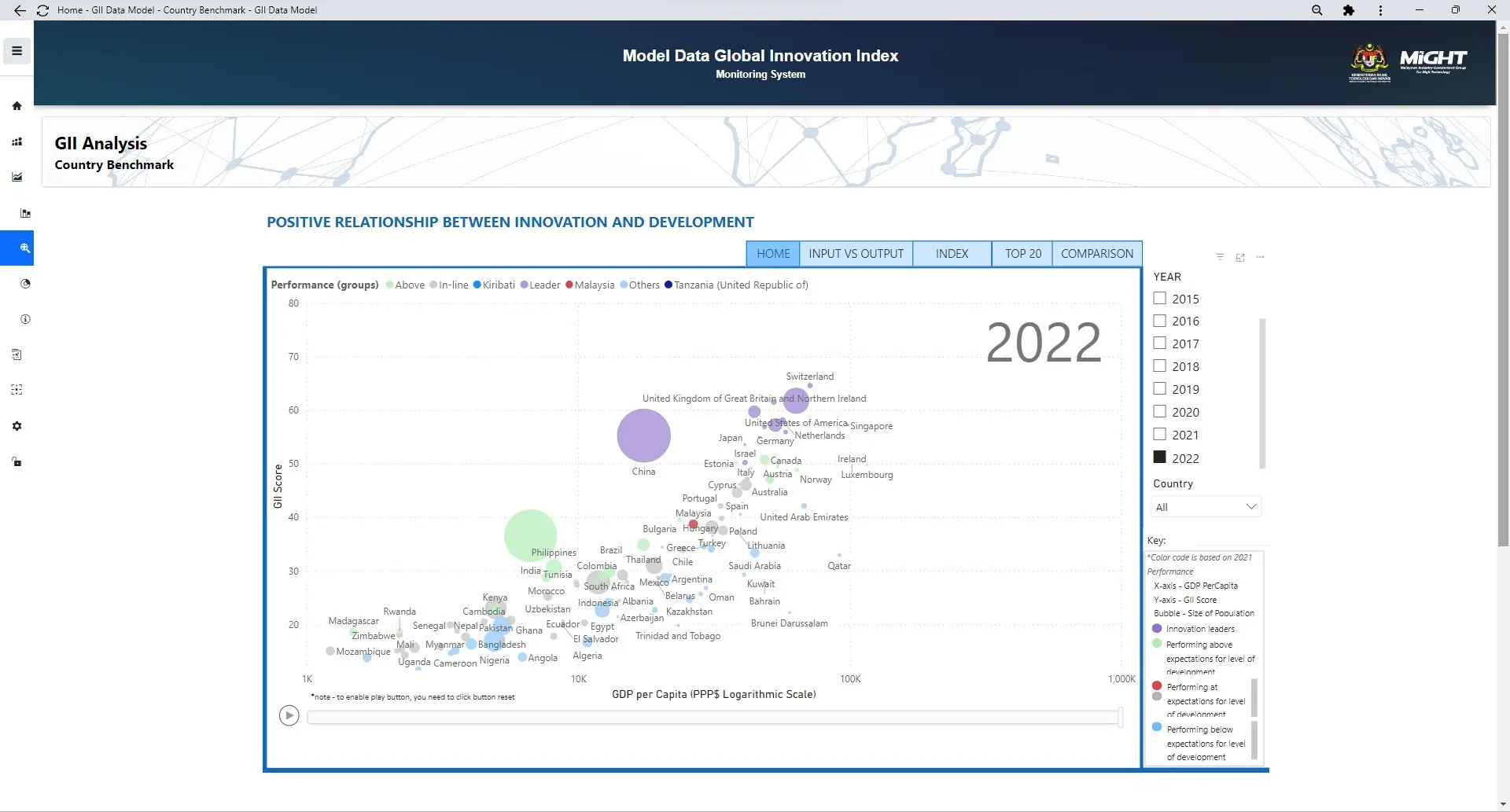
GII Country Benchmark
This module is intended to display data through visualization, making it easier for users to understand the presented statistics/information. This model allows users to access reports on Malaysia'… Read More
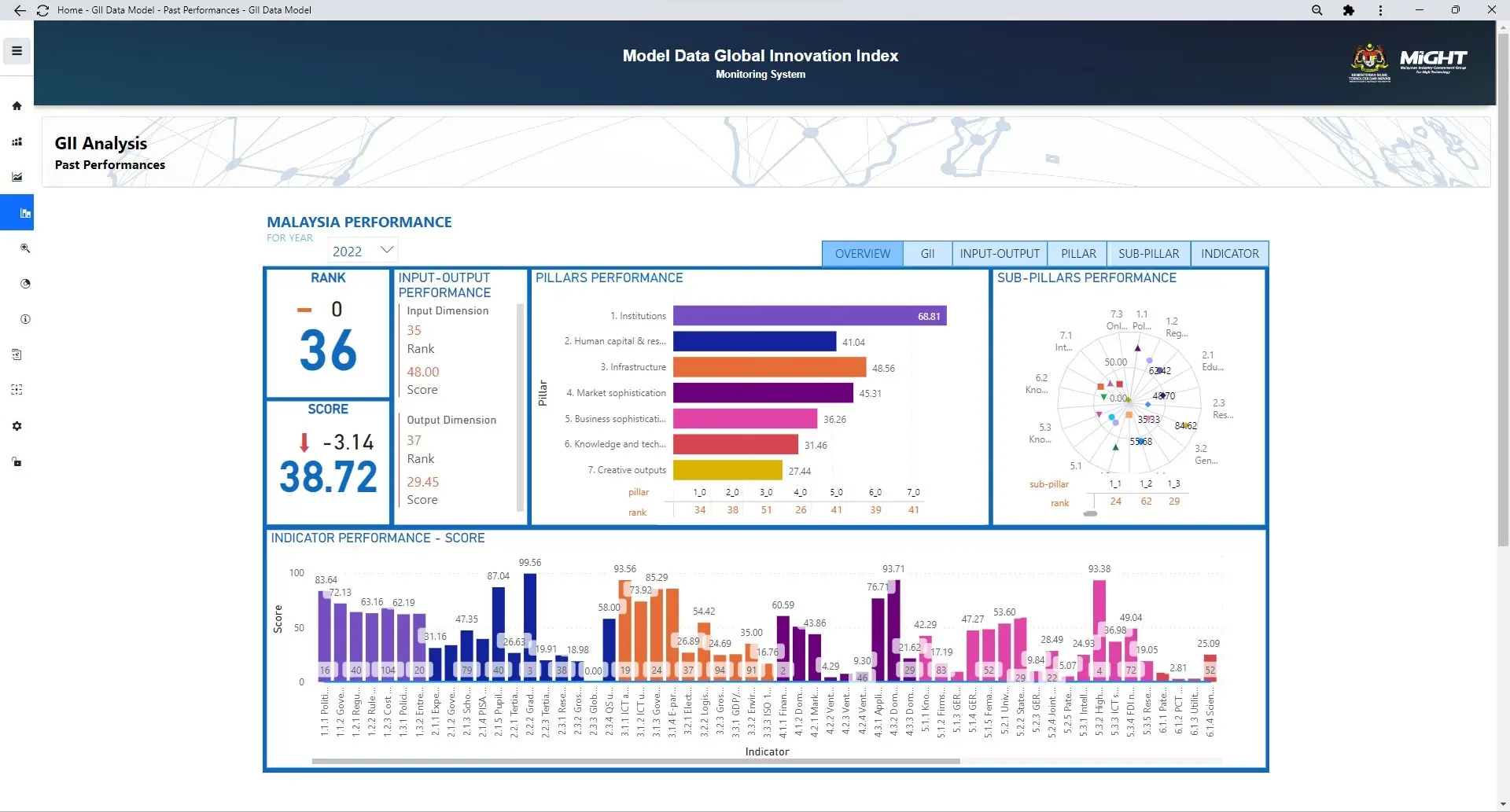
GII Past Performances
Module Tracking is a module for storing information regarding the availability years for each GII indicator of Malaysia and the years utilized by other countries. This module is intended to track… Read More
Source : Sistem Model Data GII
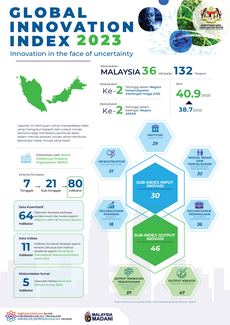
Infographic Malaysia Innovation Information
#Infographics GII 2023 is in progress

About JIPGII
The Inter-Agency GII Competitiveness Monitoring Committee (JIPGII)
Established in January 2021, the formation of this Committee is an initiative by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Innovation (MOSTI), aligned with the Government's aspiration in the Twelfth Malaysia Plan (12MP) to position Malaysia among the top 20 countries in the Global Innovation Index (GII) by the year 2025. The establishment of this committee is also seen as capable of providing impact and added value to the nation's innovation ecosystem, further enhancing the country's innovation performance effectively and efficiently through integrated inter-agency cooperation involving various ministries, departments, agencies, and private entities.
Through this committee, collaborative ties with the GII report publisher, particularly WIPO, can be established through strategic cooperation with the Intellectual Property Corporation of Malaysia (MyIPO), which is a WIPO member state.
The objective of establishing JIPGII:
- To implement and enhance the monitoring of competitiveness indices in a more systematic and effective manner to improve the country's performance in the Global Innovation Index (GII) report;
- To ensure the accuracy and timely collection, storage, and updating of indicators by data custodians in the international database, thereby showcasing the actual achievements of the country; and
- To identify short-term, mid-term, and long-term targets to improve scores and elevate Malaysia's position in the GII report.
3 PHASE: REALISING MALAYSIA’S ASPIRATION IN GII
Implementation phase and current status
PHASE 1a: MAPPING MALAYSIA'S STATE OF INNOVATION (√ DONE)
Objective: Establishing Malaysia's innovation ecosystem with its source and contribution of data to ensure comprehensiveness, accuracy and timeliness.
 PHASE 1b: COMMUNICATION MALAYSIA'S STATE OF INNOVATION (√ DONE)
PHASE 1b: COMMUNICATION MALAYSIA'S STATE OF INNOVATION (√ DONE)
Objective:
- Coordinating the relay of data information required for GII indicators in a timely manner by National data custodians to the respective international databases and
- Informing National Stakeholders on Malaysia's innovation strategies, initiatives and performance.
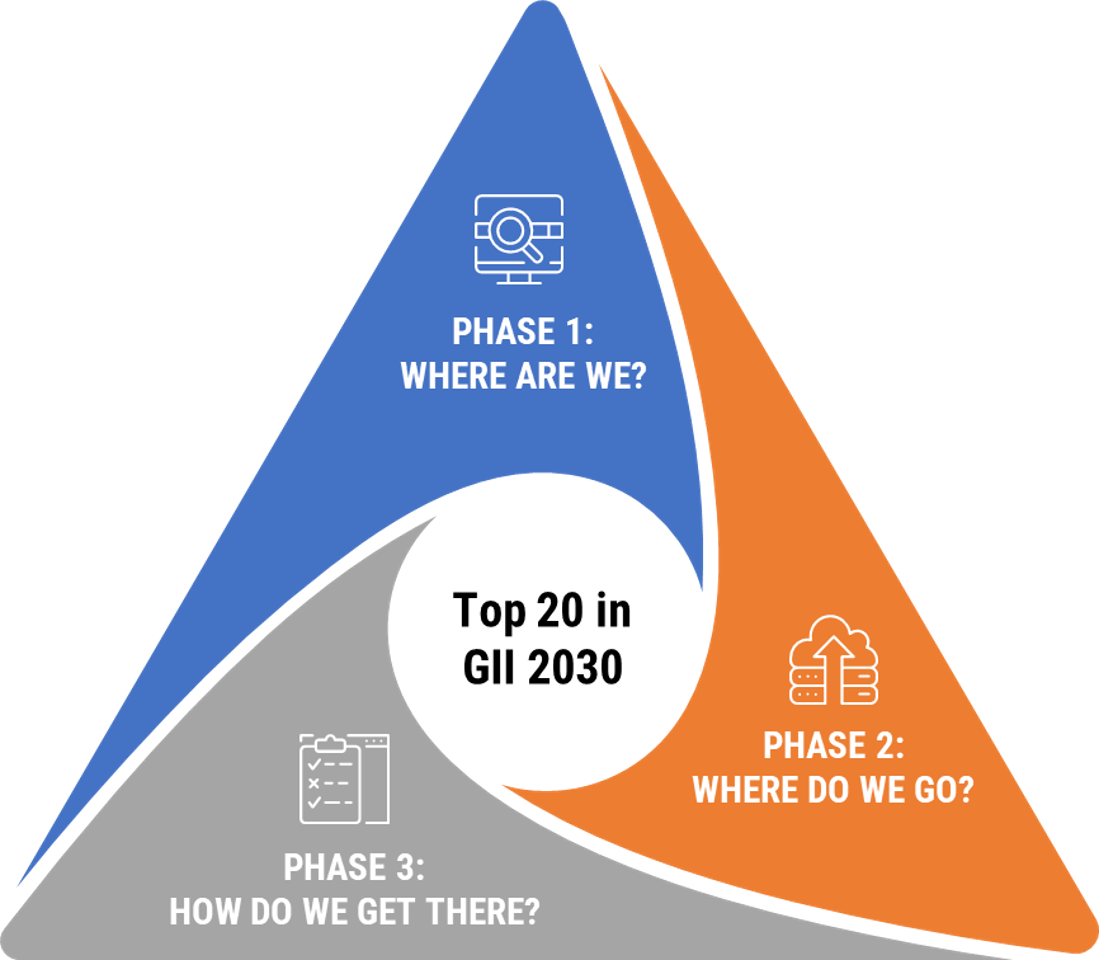
PHASE 2: ASPIRING FOR MALAYSIA'S STATE OF INNOVATION (√ DONE)
Objective:
- Benchmarking against global best practices of the GII and
- Setting the targets for Malaysia's aspiration in GII.
(Currently we are at this stage!)
PHASE 3a: MONITORING MALAYSIA'S STATE OF INNOVATION
Objective:
- Ensuring the strategies and initiatives are on track and recommending and
- Updating annual data of the GII indicators.
PHASE 3b: IMPROVING MALAYSIA'S STATE OF INNOVATION
Objective: Identifying short, mid and long-term strategies and implementing initiatives towards improving Malaysia's GII scores and ranking.
JIPGII Members
Pillar Lead: MRANTI
Ministries
- NRECC
- KKD
- MOT
- MOF
Agencies
- MCMC
- DOSM
- MAMPU
- MDEC
- JSM
- ST
Pillar Lead: MTDC
Ministries
- -
Agencies
- BNM
- BURSA MALAYSIA
- SECCOM
Pillar Lead: Cradle
Ministries
- MOHR
- MOHE
- MOF
- MITI
- MOSTI
- MASTIC
- Bhg. DANA
Agencies
- MIDA
- ASM
- MyIPO
- DOSM
- MPC
- BNM
- JPK
- MDEC
Pillar Lead: MyIPO
Ministries
- MOHE
- MITI
- MOF
- MOSTI
- Bhg. PTK
Agencies
- DOSM
- JSM
- MCMC
- PSM
- MRANTI
Pillar Lead: MIMOS
Ministries
- KKD
Agencies
- MATRADE
- MAMPU
- MyIPO
- MPC
- MYNIC
- DOSM
History
Mid-Term Review, Twelfth Malaysia Plan - Malaysia to Target GII TOP 20th by 2025

11 Sep 2023
The Global Innovation Index 2023 Launch: Innovation in the Face of Uncertainty

27 Sep 2023
GII FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
The purpose of having a Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section here is to offer succinct and useful responses to commonly raised inquiries by users or customers regarding the Global Innovation Index (GII), the Inter-Agency GII Competitiveness Monitoring Committee (JIPGII), and MOSTI's initiatives in enhancing GII competitiveness performance.

a. Menganalisa prestasi ekosistem inovasi 132 negara.
b. Menyediakan kerangka kerja berdasarkan kepada tujuh teras bagi setiap negara untuk memperbaiki ekosistem inovasi masing-masing.
c. Menyediakan penandaaras berhubung polisi dan amalan terbaik dari perspektif inovasi untuk meningkatkan daya saing sesebuah negara di peringkat antarabangsa.
Indeks ini mengukur ekosistem inovasi dalam ekonomi negara dan memberikan maklumat tentang kekuatan dan kelemahan negara dalam bidang inovasi. Sebilangan besar negara menggunakan GII untuk menilai dan menambah baik ekosistem inovasi mereka dan menggunakan GII sebagai rujukan dalam rancangan dan/atau dasar ekonomi.
GII adalah laporan daya saing inovasi di peringkat antarabangsa yang diterbitkan oleh World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Cornell University dan INSEAD. Laporan ini diterbitkan setiap tahun sejak tahun 2007.
Bilangan indikator yang dinilai dalam GII adalah sebanyak 81 indikator untuk tahun 2022. Bilangan indikator mungkin sama atau berbeza bagi setiap tahun tertakluk kepada metodologi yang diguna pakai oleh WIPO bagi tahun berkenaan.
Innovation Input Sub-Index merujuk kepada faktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi keupayaan negara untuk mencipta inovasi seperti sumber daya manusia, penelitian dan pembangunan, dan infrastruktur.
Innovation Output Sub-Index merujuk kepada hasil-hasil yang dihasilkan oleh negara dalam bidang inovasi seperti produk dan perkhidmatan, eksport teknologi tinggi paten dan sebagainya.
Terdapat tiga (3) jenis data yang diguna pakai dalam penilaian data GII iaitu:
a. Data kuantitatif/objektif/hard data: Merupakan data-data yang diperoleh daripada sumber awam dan swasta seperti UNESCO, WIPO, Thomsom Reuters dan lain-lain.;
b. Data komposit/indeks: Merupakan data-data komposit daripada agensi tertentu dan institusi akademik seperti World Bank, UN Public Administration Network (UNPAN), International Communication Union dan lain-lain.; dan
c. Data kualitatif/survei/soft data: Merupakan data-data yang diperoleh daripada soal selidik seperti Executive Opinion Survey yang dikendalikan World Economic Forum, Perbadanan Produktiviti Malaysia dan lain-lain.
Kerangka kerja GII terbahagi kepada dua (2) Sub-Index iaitu Innovation Input dan Innovation Output. Perincian adalah seperti yang berikut:
a) Innovation Input Sub-Index: Lima (5) Pillar iaitu Institutions, Human capital and research, Infrastructure, Market sophistication dan Business sophistication.
b) Innovation Output Sub-Index: Dua (2) Pillar iaitu Knowledge and technology outputs dan Creative outputs.
a. Kedudukan 20 ekonomi teratas pada tahun 2025 (RMKe-12).
b. Kedudukan 20 ekonomi teratas di bawah Pillar Knowledge and Technology pada tahun 2030 (MyDigital).
c. Skor 40-42 dalam Prestasi Petunjuk Prestasi Utama Ketua-Ketua Setiausa, Ketua-Ketua Pengarah, Setiausaha-Setiausaha Kerajaan Persekutuan dan Negeri.
Kedudukan GII sesebuah negara ditentukan dengan mengambil kira purata skor di antara Innovation Input Sub-Index dan Innovation Output Sub-Index. Ia menunjukkan sejauh mana input inovasi yang dilaksanakan mempengaruhi output inovasi bagi sesebuah negara.
Kaedah yang digunakan dalam pengukuran indeks GII adalah Purata Wajaran (Weighted Average). Pemberat yang digunapakai bagi pengiraan indeks GII adalah 0.5 dan 1.0 bergantung kepada jenis indikator. Untuk penerangan terperinci sila rujuk Nota Teknikal Laporan GII.
Definisi bagi setiap indikator boleh diperoleh daripada Appendix- Sources and Definition dalam Laporan GII.
Jumlah ekonomi/negara yang terlibat dalam penilaian mungkin sama atau berbeza pada setiap tahun. Pada tahun 2022, jumlah ekonomi yang terlibat adalah sebanyak 132 buah negara. Sesebuah negara hanya layak untuk dinilai sekiranya mempunyai liputan data sekurang-kurangnya 66% untuk Innovation Input Sub-Index dan 66% untuk Innovation Output Sub-Index.
a) Prestasi sebenar negara terlibat;
b) Penyelarasan rangka kerja GII;
c) Pengemaskinian data, treatment of outlier serta missing data; dan
d) Negara yang terlibat dalam penilaian.
a) Memberikan gambaran komprehensif berhubung ekosistem inovasi sesebuah negara.
b) Sumber maklumat berhubung amalan terbaik, penandaaras insiatif yang telah dilaksanakan oleh negara peneraju inovasi dan trend inovasi terkini di peringkat antarabangsa.
c) Sumber maklumat kepada syarikat-syarikat antarabangsa dalam proses mengenal pasti negara yang bersesuaian untuk mereka membuat pelaburan jangka masa panjang.
Malaysia tidak menyumbang data secara terus kepada WIPO. Data yang digunakan oleh WIPO hanya diambil daripada pelbagai sumber organisasi antarabangsa (seperti laporan dan pangkalan data).
Malaysia telah menjadikan GII sebagai penanda aras bagi pengukuran inovasi negara. Malaysia telah tersenarai dalam penilaian Laporan GII sejak tahun 2007.
Switzerland merupakan negara paling berinovatif di dunia bagi 12 tahun berturut-turut diikuti dengan negara Amerika Syarikat, Sweden, United Kingdom dan Belanda.
Tahap kecekapan negara sekiranya diukur daripada kualiti inovasi adalah setanding dengan negara ekonomi berpendapatan tinggi. Walau bagaimanapun, ia adalah rendah disebabkan oleh penghasilan output inovasi yang lebih rendah berbanding tahap pelaburan inovasi (input).
Prestasi Malaysia dalam GII secara keseluruhannya berada dalam lingkungan 32 ke 37. Kedudukan terbaik negara adalah ke-32 pada tahun 2012, 2013 dan 2015 manakala kedudukan terendah adalah ke-37 pada tahun 2017. Walau bagaimanapun, skor keseluruhan mencatatkan penurunan daripada 45.9% pada tahun 2012 kepada 38.7 pada tahun 2022.
Tujuan penubuhan Jawatankuasa ini adalah untuk melaksana dan menambahbaik pemantauan ke atas indeks daya saing supaya lebih sistematik dan berkesan dalam meningkatkan prestasi negara dalam Laporan GII. Penubuhan Jawatankuasa ini juga merupakan inisiatif MOSTI selaras dengan hasrat Kerajaan dalam Rancangan Malaysia Kedua belas (RMKe12) untuk meletakkan Malaysia dalam kalangan 20 negara terbaik dalam Laporan GII menjelang tahun 2025.
Menurut satu kajian oleh OECD, beberapa tindakan penting yang perlu diambil untuk meningkatkan keupayaan inovasi sesebuah negara adalah dengan melaksanakan strategi pembangunan berasaskan inovasi dan intervensi kerjasama antara Kerajaan dan swasta bagi meningkatan kadar FDI negara secara berterusan dalam pembangunan sumber manusia dan kemahiran, sains, teknologi dan inovasi.
Terdapat tiga (3) fasa pelaksanaan bagi Jawatankuasa iaitu:
a) Fasa 1: Di mana Malaysia - Pemetaan dan komunikasi tahap inovasi negara untuk mengenal pasti ekosistem inovasi Malaysia berdasarkan sumber dan penyumbang data bagi memastikan data yang komprehensif, tepat dan terkini serta menyelaras penyampaian maklumat dan data yang diperlukan bagi indikator GII tepat pada masanya oleh penyumbang data nasional kepada pangkalan data antarabangsa;
b) Fasa 2: Di mana arah laluan Malaysia - Aspirasi tahap inovasi negara untuk penandaarasan amalan terbaik global dan menetapkan sasaran untuk aspirasi Malaysia dalam GII; dan
c) Fasa 3: Bagaimana untuk mencapai sasaran - Meningkatkan dan memantau tahap inovasi negara untuk mengenal pasti strategi jangka pendek, pertengahan dan jangka panjang dan melaksanakan inisiatif untuk meningkatkan skor dan kedudukan GII Malaysia serta memastikan strategi dan inisiatif berada di landasan yang betul dan mengesyorkan langkah-langkah pembetulan jika diperlukan.
Ya, sebarang pertukaran pegawai yang telah dilantik bagi mewakili Kementerian/Agensi perlu dimaklumkan kepada pihak MOSTI bagi tujuan rekod.
Keutamaan Pegawai yang sesuai untuk dicalonkan bagi mewakili Kementerian/Agensi dalam Jawatankuasa ini ialah Pegawai Gred 48 dan ke atas. Walau bagaimanapun, Pegawai kumpulan P&P daripada Gred 41/44 juga boleh dicalonkan jika bidang tugas melibatkan pengurusan dasar/polisit/KPI dan strategik Kementerian/Agensi tersebut.
Urus Setia bagi Jawatankuasa ini adalah Pusat Maklumat Sains dan Teknologi Malaysia (MASTIC) dan Malaysian Industry-Government Group for High Technology (MIGHT).
Jawatankuasa ini akan bersidang sekurang-kurangnya dua (2) kali setahun iaitu pada Q2 (April-Jun) dan Q4 (Oktober-Disember).
Punca kuasa penubuhan Jawatankuasa ini adalah daripada Keputusan Mesyuarat Majlis Inovasi Negara yang memutuskan supaya sebuah Jawatankuasa yang diterajui oleh MOSTI ditubuhkan untuk memantau pelaksanaan inisiatif oleh Kementerian/Agensi bagi meningkatkan indikator di bawah bidang masing-masing.
Jawatankuasa ini dipengerusikan oleh Timbalan Ketua Setiausaha MOSTI dan terdiri daripada tujuh (7) Jawatankuasa Kumpulan Kerja (JKK) seperti berikut:
a). JKK Pillar Institutions;
b). JKK Pillar Human Capital & Research;
c). JKK Pillar Infrastructure;
d). JKK Pillar Market Sophistication;
e). JKK Pillar Business Sophistication;
f). JKK Pillar Knowledge & Technology Outputs; dan
g). JKK Pillar Creative Outputs.
JIPGII adalah sebuah Jawatankuasa yang ditubuhkan oleh MOSTI sejak bulan Januari tahun 2021.
Ya, kesemua Kementerian/Agensi/Jabatan terlibat dalam GII. Kementerian/Agensi/Jabatan yang mempunyai indikator dan menyalurkan data secara terus dengan GII terlibat secara langsung dengan GII.
Walau bagaimanapun, terdapat Kementerian/Agensi/Jabatan lain yang turut menyumbang secara tidak langsung contohnya seperti pelaksana polisi yang turut menyumbang kepada ekosistem ekonomi negara.
Pembekal data untuk GII terdiri daripada Kementerian/Agensi/Jabatan/syarikat/individu yang mengemukakan data kepada badan penarafan antarabangsa. Data-data yang dibekalkan adalah daripada jenis hard data.
Sumber data yang digunakan oleh pihak penerbit diakses melalui Appendix dalam Laporan GII.
Sebanyak 12 indikator telah dikenal pasti mempunyai sasaran high-priority dalam polisi Kementerian/Agensi dan 14 indikator pula dikategorikan sebagai medium high-priority. Selain indikator tersebut adalah dalam kategori low-priority.
Tarikh akhir untuk mengemukakan maklumat/data kepada pihak MOSTI atau Badan Pengumpul Data Antarabangsa sebelum skor dan kedudukan GII sesebuah negara dianalisis oleh WIPO ialah bermula selepas pelancaran Laporan GII (Sekitar Bulan September) sehingga selewat-lewatnya pada Bulan Mac Tahun berikutnya.
Antara inisiatif, program atau projek yang boleh dipertimbangkan adalah yang berkaitan dengan KPI Kementerian dan turut menyumbang secara langsung atau tidak langsung dengan peningkatan prestasi negara dalam GII.
Sesetengah indikator juga bergantung kepada 'secondary macro indicator' contohnya GDP/unit tenaga yang digunakan. Indikator yang patut diberi penekanan adalah indikator utama (Contohnya: unit tenaga).
Maklumat inisiatif, program atau projek yang disenaraikan perlu mengambil kira skop, KPI, sasaran, outcome yang mempunyai impak kepada prestasi GII.
Maklumat yang perlu dikongsikan dengan MOSTI adalah maklumat berkaitan inisiatif, program atau projek yang dilaksanakan oleh Kementerian/ Agensi yang menyumbang kepada peningkatan prestasi dalam GII. Maklumat yang dikongsikan ini perlulah berkaitan dengan indikator GII (inisiatif oleh Kementerian).
Inisiatif pengumpulan data ini bertujuan untuk mengenalpasti dan mengemaskini pemilik data berkaitan serta memantau prestasi setiap indikator dalam Laporan GII melalui inisiatif/ program yang telah dilaksanakan di bawah Kementerian, Jabatan dan Agensi masing-masing. Maklumat yang dikumpulkan ini akan dikunci masuk ke dalam Sistem Model Data GII bagi tujuan pemantauan.
i). Prestasi negara yang semakin menurun terutamanya dari segi skor;
ii). Polisi berkaitan GII yang tidak mencukupi; dan
iii). Prestasi terkini berkaitan compound annual growth rate (CAGR) yang rendah iaitu sekitar 3.18% berbanding CAGR yang perlu dicapai untuk mencapai kedudukan 20 teratas iaitu 11.19%.
MOSTI menyalurkan data secara terus kepada MPC selaku Partner Institute kepada Laporan WCY bagi data-data berkaitan Kajian Penyelidikan dan Pembangunan (R&D) Kebangsaan. Data yang dilaporkan dalam Laporan WCY juga turut dilaporkan dalam GCR.
MOSTI sedang melaksanakan inisiatif pengumpulan maklumat program atau projek yang berkaitan dengan semua 81 indikator yang diukur dalam GII bagi kesemua Kementerian/Agensi melalui surat Ketua Setiausaha Kementerian yang bertarikh 15 Jun 2023.
Sistem Model Data GII dibangunkan oleh MOSTI dengan kerjasama rakan strategiknya iaitu MIGHT. Sistem Model Data GII ini boleh diakses melalui pautan gii.mosti.gov.my Sistem Model Data ini dibangunkan bertujuan sebagai kaedah kuantitatif penanda aras (Benchmarking) bagi mengukur tahap pencapaian inovasi negara berbanding negara-negara di seluruh dunia. Selain itu, Sistem Model Data ini juga sesuai digunakan sebagai medium pemantauan dan sumber panduan dalam proses membuat keputusan berdasarkan fakta berkaitan dasar/polisi/perancangan inisiatif/projek dan program. Sistem Model Data ini mengandungi maklumat terperinci seperti dashboard dan simulasi skor dan kedududukan negara, deskripsi dan sumber data diperolehi berbanding dengan negara-negara lain dalam tempoh 10 tahun (2013-2022). Untuk maklumat lanjut berkaitan Sistem Model Data ini sila berhubung dengan Urus Setia JIPGII di Talian Telefon: 03-8885 8652.
Pillar Lead yang dilantik bertanggungjawab untuk mengadakan sesi libat urus bersama-sama ahli di bawah. Selain itu, Bengkel Scenario Building GII telah diadakan yang diuruskan oleh MIGHT dan MOSTI mengikut Pillar seperti berikut:
i). Pillar Infrastructure: 28 September 2022
ii). Pillar Human Capital & Research: 18 Oktober 2022
iii). Pillar Creative Outputs: 26 Oktober 2022
iv). Pillar Market Sophistication: 27 Oktober 2022
v). Pillar Institutions: 1 November 2022
vi). Pillar Knowledge & Technology Outputs: 2 November 2022
vii). Pillar Business Sophistication: 10 November 2022
Maklumat pemilik dan penyumbang data berkaitan indikator GII akan dikemaskini dari masa ke masa dan pemantauan berterusan akan dilaksanakan untuk inisiatif yang telah dikenal pasti bagi melonjakkan prestasi negara dalam GII. Pendekatan ‘whole of government approach’ juga akan dilaksanakan bagi memperoleh kerjasama yang padu dan maklumat yang bersepadu daripada segenap sudut.
Maklumat/data boleh disalurkan kepada pegawai MOSTI yang berikut:
1.Nama : Puan Noor Fairuz Binti Shamsudin
E-mel/No. Tel. : noorfairuz@mosti.gov.my / 03-8885 8110
2.Nama : Encik Rudy Bin Nurdin
E-mel/No. Tel. : rudy@mosti.gov.my / 03-8885 8652
GII Reports Compilation
Reports on the Global Innovation Index (2007 - 2023)
Welcome to the Collection of Global Innovation Index Reports!
Dear readers and innovators, It is with great pleasure and enthusiasm that we open the doors to the prestigious collection of Global Innovation Index Reports. The Global Innovation Index (GII) is an annual report that has been published since 2007 and provides a comprehensive framework and a set of indicators to measure innovation performance of countries and economies around the world according to their innovation capabilities and outcomes, identifies their strengths and weaknesses, provides policy recommendations and best practices to foster innovation.
The GII report covers a wide range of topics related to innovation, including:
- Innovation Rankings:
The GII ranks countries based on their overall innovation performance. It provides a comparative analysis of how nations are faring in terms of fostering innovation.
- Innovation Inputs:
The report assesses the inputs and enablers that contribute to a country's innovation capabilities, such as investments in education, R&D, infrastructure, and information and communication technology (ICT).
- Innovation Outputs:
The GII evaluates the tangible and measurable results of innovation efforts, such as patents, publications, creative products, and high-tech exports.
- Innovation Policy Analysis:
The report analyzes innovation policies and strategies implemented by countries to support and encourage innovation within their respective economies.
- Innovation Impact:
The GII examines the impact of innovation on economic growth, productivity, and other developmental outcomes.
You can find more information about the GII reports from 2007 until 2023 below.
Together, let us unleash the potential of innovation and forge a world that knows no bounds

The Global Innovation Index 2023 (GII) takes the pulse of innovation against a background of an economic and geopolitical environment fraught with…
16thed.: 2023
New Ed. (Released on 27 Sept 2023)

Global Innovation Index 2022 (GII) tracks global innovation trends against the background of an ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, slowing productivity…
15thed.: 2022
(Released on 27 Sept 2022)

The Global Innovation Index 2021 takes the pulse of the most recent global innovation trends and ranks the innovation ecosystem performance of 132…
14th ed.: 2021

The Global Innovation Index 2020 provides detailed metrics about the innovation performance of 131 countries and economies around the world.
13th ed.: 2020

The Global Innovation Index 2019 provides detailed metrics about the innovation performance of 129 countries and economies around the world.
12th ed.: 2019

The Global Innovation Index 2018 provides detailed metrics about the innovation performance of 126 countries and economies around the world.
11th ed.: 2018
Contact Secretariat
GII Data Managment
Hi! Im MYGII

MASTIC

Administrator
Noor Fairuz Shamsudin
03-8885 8110
noorfairuz@mosti.gov.my

Administrator
Rudy Nurdin
03-8885 8652
rudy@mosti.gov.my
Help us with this survey
Please make your vote
Agency
Pillar Lead JIPGII
Pillar 1
Institution

Malaysia Productivity Corporation
Ilyana Norsaidah
Person In Charge
illyana@mpc.gov.my
03 - 7955 7266
Pillar 2
Human Capital & Research

Akademi Sains Malaysia
Teng Yu He
Person In Charge
teng@akademisains.gov.my
03 - 6203 0633
Pillar 3
Infrastructure

Malaysian Research Accelerator for Technology & Innovation
Nur Aliya Ayob
Person In Charge
aliya@mranti.my
03 - 8998 2020
Pillar 4
Market Sophistication

Malaysia Technology Development Corporation
Nor Halina Ghazali
Person In Charge
halina@mtdc.com.my
03 - 2172 6000
Pillar 5
Business Sophistication

Cradle Fund Sdn. Bhd.
Sitti Nursaadah Md Rusli
Person In Charge
sitti@cradle.com.my
03 - 4045 8600
Pillar 6
Knowledge & Technology Outputs

Intellectual Property Corporation of Malaysia
Meriam Nur Ahmad Hanbali
Person In Charge
meriam@myipo.gov.my
03 - 2299 8961
Pillar 7
Creative Outputs

Malaysian Institute of Microelectronic Systems
Siti Affida Zamry
Person In Charge
affida@mimos.my
03 - 8995 5000